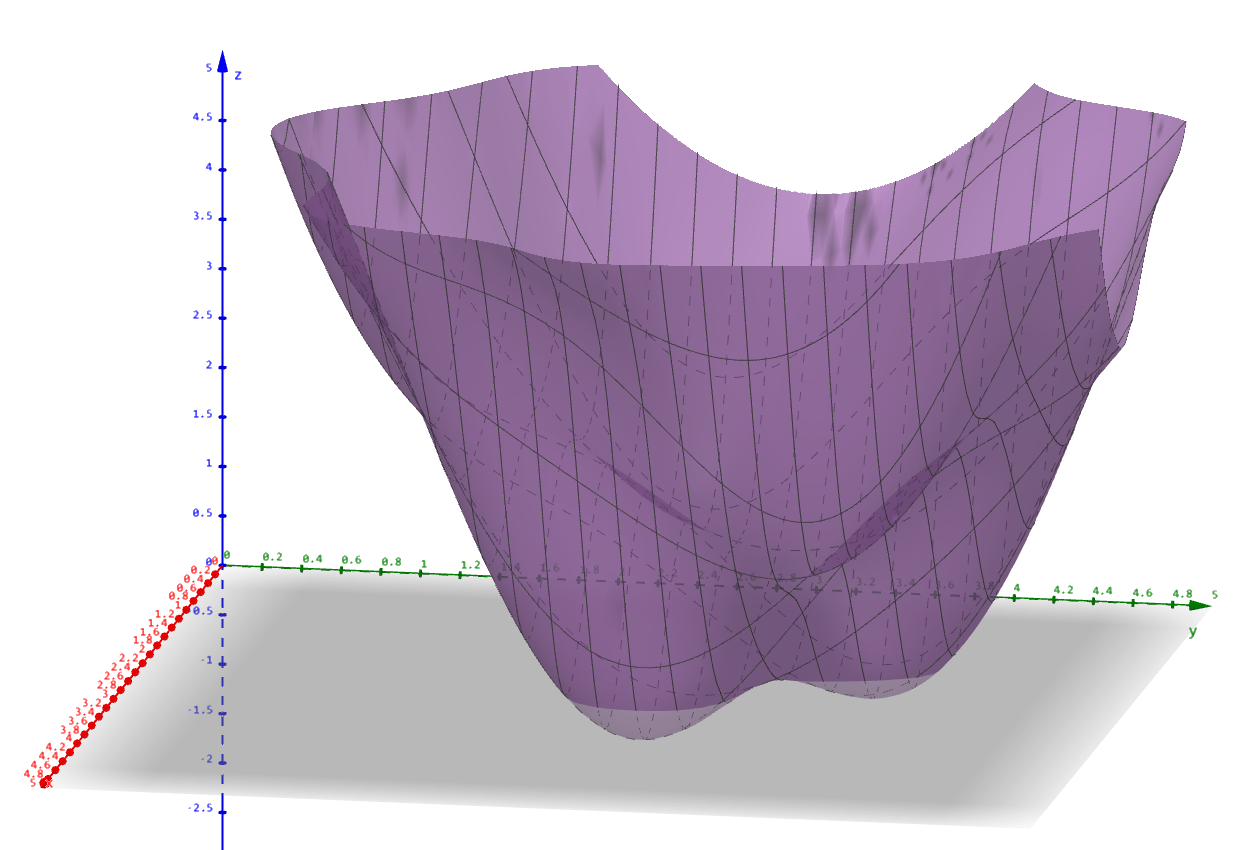
问题: min_{x \in [0,5]^2} f(x)=(x_1-2)^2+(x_2-3)^2+sin(3x_1)sin(2x_2)
方法A:网格/随机重启的局部搜索
思路:
-
在 [0,5]^2 里随机选一个点;
-
看四个方向 (x_1 \pm step,x_2 \pm step) 有没有更小的 f;
-
有就走过去,继续找;
-
一直走到“周围都不下降为止“(局部最优);
-
为了避免卡在局部解,多随机重启几次,取最好的一次。
Code
# 目标函数
def f(x1, x2):
return (x1 - 2) ** 2 + (x2 - 3) ** 2 + math.sin(3 * x1) * math.sin(2 * x2)
def f_vec(x):
return f(x[0], x[1])
BOUNDS = [(0.0, 5.0), (0.0, 5.0)]
# 随机重启局部搜索
def local_search_once(max_iters=200, step=0.05):
x = [random.uniform(*BOUNDS[0]), random.uniform(*BOUNDS[1])]
fx = f_vec(x)
for _ in range(max_iters):
improved = False
for dim in (0, 1):
# 四个邻居:x1 +- step, x2 +- step
for direction in (-1, 1):
cand = x.copy()
cand[dim] += step * direction
# 边界截断到 [0,5]
cand[dim] = max(BOUNDS[dim][0], min(BOUNDS[dim][1], cand[dim]))
f_cand = f_vec(cand)
if f_cand < fx:
x, fx = cand, f_cand
improved = True
break
if not improved:
break # 附近没有更好的点,认为到达局部最优
return x, fx
def random_restart(num_restarts=20, **kwargs):
best_x, best_f = None, float("inf")
for _ in range(num_restarts):
x, fx = local_search_once(**kwargs)
if fx < best_f:
best_f, best_x = fx, x
return best_x, best_f方法B:微型GA
Code
# 微型GA
def ga_once(pop_size=20, generations=20, crossover_p=0.8, mutation_p=0.3, mutation_sigma=0.1):
# 初始化种群:均匀随机
pop = [[random.uniform(*BOUNDS[0]), random.uniform(*BOUNDS[1])] for _ in range(pop_size)]
def fitnses(ind):
# 因为要 “最小化 f”,可以把适应度设成 -f
return -f_vec(ind)
for _ in range(generations):
# 计算适应度
fits = [fitnses(ind) for ind in pop]
# 锦标赛选择
def select():
i, j = random.randrange(pop_size), random.randrange(pop_size)
return pop[i] if fits[i] > fits[j] else pop[j]
new_pop = []
while len(new_pop) < pop_size:
p1, p2 = select(), select()
# 交叉:简单线性交叉
if random.random() < crossover_p:
alpha = random.random()
c1 = [alpha * a + (1 - alpha) * b for a, b in zip(p1, p2)]
c2 = [alpha * b + (1 - alpha) * a for a, b in zip(p1, p2)]
else:
c1, c2 = p1[:], p2[:]
# 变异:对某一维加一点高斯噪声,再截断回区间
for c in (c1, c2):
if random.random() < mutation_p:
d = random.randrange(2)
c[d] += random.gauss(0, mutation_sigma)
c[d] = max(BOUNDS[d][0], min(BOUNDS[d][1], c[d]))
new_pop.append(c)
if len(new_pop) >= pop_size:
break
pop = new_pop
# 返回种群里 f 最小的个体
best = min(pop, key=f_vec)
return best, f_vec(best)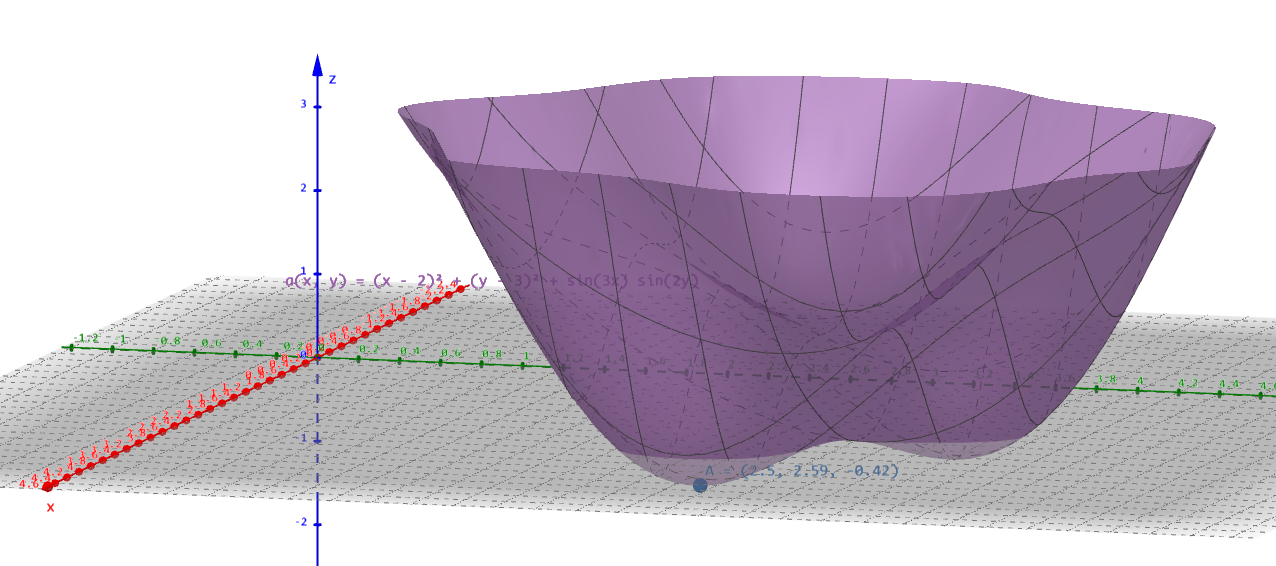
完整代码
import math
import random
import time
import statistics as st
# 目标函数
def f(x1, x2):
return (x1 - 2) ** 2 + (x2 - 3) ** 2 + math.sin(3 * x1) * math.sin(2 * x2)
def f_vec(x):
return f(x[0], x[1])
BOUNDS = [(0.0, 5.0), (0.0, 5.0)]
# 随机重启局部搜索
def local_search_once(max_iters=200, step=0.05):
x = [random.uniform(*BOUNDS[0]), random.uniform(*BOUNDS[1])]
fx = f_vec(x)
for _ in range(max_iters):
improved = False
for dim in (0, 1):
# 四个邻居:x1 +- step, x2 +- step
for direction in (-1, 1):
cand = x.copy()
cand[dim] += step * direction
# 边界截断到 [0,5]
cand[dim] = max(BOUNDS[dim][0], min(BOUNDS[dim][1], cand[dim]))
f_cand = f_vec(cand)
if f_cand < fx:
x, fx = cand, f_cand
improved = True
break
if not improved:
break # 附近没有更好的点,认为到达局部最优
return x, fx
def random_restart(num_restarts=20, **kwargs):
best_x, best_f = None, float("inf")
for _ in range(num_restarts):
x, fx = local_search_once(**kwargs)
if fx < best_f:
best_f, best_x = fx, x
return best_x, best_f
# 微型GA
def ga_once(pop_size=20, generations=20, crossover_p=0.8, mutation_p=0.3, mutation_sigma=0.1):
# 初始化种群:均匀随机
pop = [[random.uniform(*BOUNDS[0]), random.uniform(*BOUNDS[1])] for _ in range(pop_size)]
def fitnses(ind):
# 因为要 “最小化 f”,可以把适应度设成 -f
return -f_vec(ind)
for _ in range(generations):
# 计算适应度
fits = [fitnses(ind) for ind in pop]
# 锦标赛选择
def select():
i, j = random.randrange(pop_size), random.randrange(pop_size)
return pop[i] if fits[i] > fits[j] else pop[j]
new_pop = []
while len(new_pop) < pop_size:
p1, p2 = select(), select()
# 交叉:简单线性交叉
if random.random() < crossover_p:
alpha = random.random()
c1 = [alpha * a + (1 - alpha) * b for a, b in zip(p1, p2)]
c2 = [alpha * b + (1 - alpha) * a for a, b in zip(p1, p2)]
else:
c1, c2 = p1[:], p2[:]
# 变异:对某一维加一点高斯噪声,再截断回区间
for c in (c1, c2):
if random.random() < mutation_p:
d = random.randrange(2)
c[d] += random.gauss(0, mutation_sigma)
c[d] = max(BOUNDS[d][0], min(BOUNDS[d][1], c[d]))
new_pop.append(c)
if len(new_pop) >= pop_size:
break
pop = new_pop
# 返回种群里 f 最小的个体
best = min(pop, key=f_vec)
return best, f_vec(best)
def repeat_exp(algo, runs=5, **kwargs):
best_vals, times, points = [], [], []
for _ in range(runs):
start = time.time()
x, fx = algo(**kwargs)
end = time.time()
best_vals.append(fx)
times.append(end - start)
points.append(x)
result = {
"best": min(best_vals),
"mean": st.mean(best_vals),
"var": st.pvariance(best_vals),
"time_mean": st.mean(times),
"time_var": st.pvariance(times),
"points": points,
"vals": best_vals
}
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
random.seed(0)
print("=== 方法 A: 随机重启局部搜索 ===")
res_A = repeat_exp(random_restart, runs=5, num_restarts=20, max_iters=200, step=0.05)
print("最优值 :", res_A["best"])
print("平均最优值 :", res_A["mean"])
print("方差 :", res_A["var"])
print("平均耗时(s):", res_A["time_mean"])
print("各次解和函数值:")
for p, v in zip(res_A["points"], res_A["vals"]):
print(" x =", p, "f(x) =", v)
print("\n=== 方法 B: 微型 GA ===")
res_B = repeat_exp(ga_once, runs=5, pop_size=20, generations=20)
print("最优值 :", res_B["best"])
print("平均最优值 :", res_B["mean"])
print("方差 :", res_B["var"])
print("平均耗时(s):", res_B["time_mean"])
print("各次解和函数值:")
for p, v in zip(res_B["points"], res_B["vals"]):
print(" x =", p, "f(x) =", v)执行结果
=== 方法 A: 随机重启局部搜索 ===
最优值 : -0.41941422122325545
平均最优值 : -0.41922770847720386
方差 : 1.9129501726128993e-08
平均耗时(s): 0.0
各次解和函数值:
x = [2.4985234320197747, 2.5941177111213416] f(x) = -0.4191540164008747
x = [2.4969566427717798, 2.5836476412777745] f(x) = -0.41941422122325545
x = [2.502945662811286, 2.5834839733110253] f(x) = -0.4190215546429824
x = [2.4924103099766644, 2.5971230304873374] f(x) = -0.4192088959066057
x = [2.495563697621402, 2.5930006503131655] f(x) = -0.4193398542123012
=== 方法 B: 微型 GA ===
最优值 : -0.4194651906149328
平均最优值 : -0.3933965480015764
方差 : 0.0026890479459860364
平均耗时(s): 0.0
各次解和函数值:
x = [2.487235715773778, 2.591029838143908] f(x) = -0.41932901439782555
x = [2.495758826529142, 2.586379125325827] f(x) = -0.4194651906149328
x = [1.6636069947209504, 3.6057467494168303] f(x) = -0.28968466883561594
x = [2.4985637149795124, 2.583793335776672] f(x) = -0.4193442196395164
x = [2.500061980308704, 2.5790775462196165] f(x) = -0.41915964651999127结论
-
局部搜索(方法 A)
-
每次都能找到 f ≈ -0.419 的解,位置在 (2.49, 2.59) 附近;
-
5 次之间的方差极小 → 很稳,不太容易掉坑;
-
时间跟步长、重启次数成正比,一般也挺快。
-
-
微型 GA(方法 B)
-
好的时候也能找到差不多的最优值;
-
但有几次会停在比较差的局部(比如 f ≈ -0.29)→ 方差更大,比较不稳定;
-
时间与种群大小、代数相关,通常也很快,但参数选得不好就白浪费代数。
-
-
谁更稳?
从 5 次结果的方差看,局部搜索更稳定,GA 对参数比较敏感,偶尔掉坑。 -
是否陷入局部最优?
-
局部搜索如果重启次数少、步长设得怪,容易卡局部(这就是为啥要随机重启);
-
GA 如果种群太小、变异率太低,也会早早收敛到局部最优。
-
-
参数敏感性?
-
局部搜索:步长 step、重启次数 num_restarts;
-
GA:种群大小 pop_size、代数 generations、交叉概率、变异概率、变异强度 sigma。
可以稍微改几个参数,看看最优值和方差怎么变,写两句感想就够了。
-

